环境配置
要使用 HTTP2 首先要安装 H2O Web 服务器。截至目前,Nginx 虽然已经支持 HTTP2,但并不支持 Server-Push。
参照官网的文档安装好 H2O 服务器,我是用 CentOS 已 yum 方式安装,安装完成后配置文件默认在 /etc/h2o/h2o.conf。
修改配置如下:
|
|
将 user 配置为 web 服务的用户名,配置 ssl 证书和私钥路径,配置 file.custom-handler 用 fastcgi 方式处理 PHP 请求。更多的配置可参考 H2O 官网的配置章节
启动服务测试
执行 service h2o start 启动服务,如无异常应当可以在浏览器中访问到页面了,可通过 service h2o status 命令查看 h2o 服务的运行情况。
在服务器根目录放置 PHP 文件 http2_server_push.php :
|
|
PHP 通过发送一个 HTTP 头: Link: <demo.png>; rel=preload; as=image 告知 H2O 将 demo.png 文件 Push 到客户端。此时打开 Chrome 的 Developer Tools,在 Network Panel 看到的瀑布流如下图:
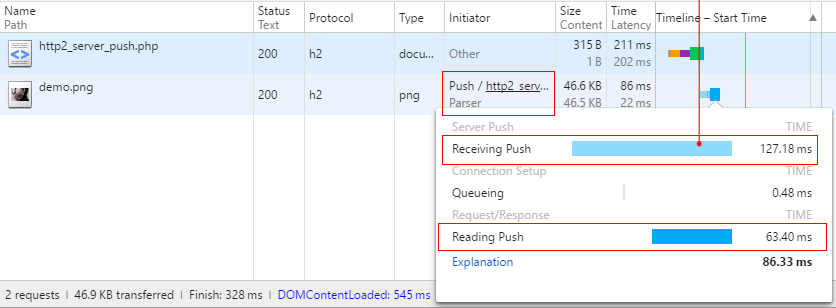
可以看到这里说明为 Push,从 Timeline 上也可以看出 demo.png 在 html 页面下载完成前已经开始接收。
将 PHP 文件中的 header 行注释掉,再次查看:
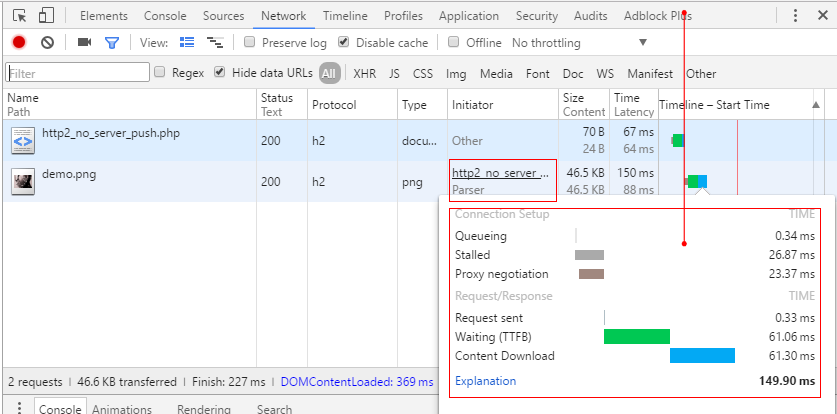
可以看出并没有 Server Push。
实际使用中可以在 PHP 中 html 输出之前使用正则方式提取页面中的静态资源链接,然后发送 Link: 头。
HTTP2 带来了一些特性,推翻了之前的前端优化原则。
- 长连接和头部压缩:不再需要将资源文件合并,因为头部浪费数据减少了,而且不会需要建立多次连接;
- 多路复用:静态文件不再需要拆分到多个域名下,放在同一个域名下还可以减少建立的连接数;
- Server Push:不再需要将重要的静态资源内联到页面中,使用 Server Push 还可以享受到浏览器的好处。
缓存问题
由于是服务端主动推送,存在的问题是可能客户端已经存在缓存了,但服务端已经开始推送,浪费了带宽。要解决这个问题首先想到的就是浏览器在发起 html 页面请求时带上一个 Cookie,标识哪些资源已经有缓存了。H2O 提供了一个叫做 cache-aware server-push 的技术来解决,原理也是相同,只是它采用了一个压缩算法来压缩 Cookie 中的信息。
参考链接
Using HTTP/2 Server Push with PHP
Google Chrome http2-push-manifest 创建 http2-push 静态资源列表
H2O 中的 Cache-Aware Server Push 简介
WordPress plugin to pre-load images using HTTP/2 Server Push